How to Log Data Wirelessly
Wirelessly monitoring instruments and sensors is becoming more and more common. A wireless network saves cabling costs and installation time. It is useful in electrically noisy or hostile environments. It lets you move your measuring device from place to place and remotely monitor conditions.
But what if your existing devices are not enabled for wireless measurements? In many cases you can make them so by adding appropriate adaptors or routers.
There are several different methods of wireless communication. The standards for many of these methods are still being developed.
- Bluetooth
- Bluetooth was designed as replacement for short-range cables. It allows up to seven devices to be monitored over short distances, typically about 10 meters. It is called a wireless Personal Area Network (PAN) and conforms to the IEEE 802.15 standard. It is suitable when devices are close to the computer and high bandwidth is not required. Bluetooth is named after a Danish king who unified Denmark and Norway.
- WiFi
-
Similar to a traditional Ethernet model, WiFi comprises
a local area network (LAN). It uses the same radio
frequency as Bluetooth, but with higher power consumption.
WiFi is preferable to Bluetooth for operating medium-to-
large networks because it allows for a faster connection
speed, greater range, more devices to be monitored and
higher security levels.
WiFi networks conform to the IEEE 802.11 specifications. The first 802.11 specifications were introduced in 1997 and these have been regularly amended. Each new version of the specification has a different letter at the end - IEEE 802.11a and IEEE 802.11be for example. The differences between the versions include the frequency at which they operate and the speed of data transfer
Most computers come with a WiFi card built-in, but if not just plug an adaptor into the USB port.
You can use instruments with RS232 ports over WiFi. To do this you need a serial device server. This will usually come with driver software which makes your instrument appear as if it were connected to the COM port. You can therefore use any data acquisition software which reads RS232 instruments to log data from your device. We of course recommend the Windmill COMIML software to automatically collect data from whatever instrument you have connected (free to our newsletter subscribers).
- LoRaWAN
- LoRaWAN stands for Long Range Wide Area Network. It wirelessly connects battery operated "things" to the internet, using radio frequency bands. For example, in Europe it uses the 863 to 870 MHz band. The stated range is 16 km in a clear line of sight and 5 km in built-up environments. The world distance record, though, is 832 km. This was made with a LoRaWAN sensor attached to a high altitude helium balloon.
The system uses very little energy when communicating with sensors. Batteries can last for 10 to 15 years.
In default mode (class A), communication is initiated by the end device (such as a sensor). The device can send data at any time. It then leaves a window to receive instructions. This is the lowest power consumption mode. In other modes the network server can also initiate communications. Modes can be switched to save power.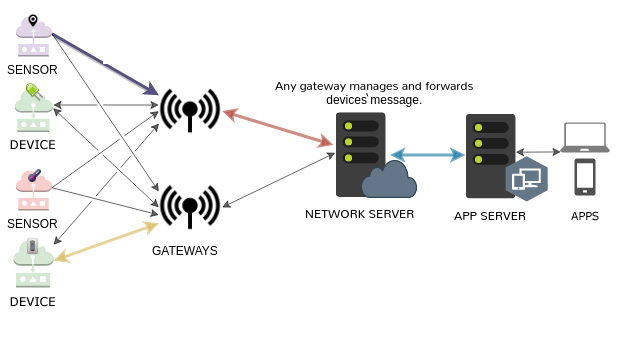
LoRaWAN architecture, modified from original image by Brivadeneira, CC by 4.0.- ZigBee
- ZigBee was designed specifically for remote monitoring and control. It comprises a personal area network based on the IEEE 8-2.15.4 standard. ZigBee can support thousands of nodes in a star or mesh network. In a star network all devices communicate with the controlling node, as is used by WiFi and Bluetooth. In a mesh network, messages can be passed from node to node such that if any of the nodes fail, the message can still reach the destination. Once associated with a network, a ZigBee node can wake up and communicate with other ZigBee devices then return to sleep. This and its low power means that a device's battery can last a very long time.
- WirelessHART
- The HART specification includes the wireless protocol dubbed WirelessHART. This sets out to create a wireless version of the Wired HART protocol in order to ensure backward compatibility with wired devices. HART Communication is used to communicate between intelligent field instruments and host systems.
- WiMax
- WiMax, the Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access, aims to provide wireless data over long distances in a variety of ways. It is based on the IEEE 802.16 standard, which is also called WirelessMAN. Typically it has a range with a radius of 3 to 10 km. The latest release, in 2021, is WiMax 3.